While writing any industry level algorithm/code or even in competitive programming one must keep in mind the complexity of it. In order to make anything scalable we must need to optimize our code for large data as much as possible.
Scalability & optimization are directly related. If your code is optimized you can scale better.
Understanding Big-O
Before knowing if we are writing optimized code, you must need to understand the problem statement, then try to solve with any approach you can no matter how bad the code is because ultimately our aim is to solve the problem in first place.
After you have successfully found the solution, now is the time to work on optimizations.
To understand optimization we must first understand how it is measured:
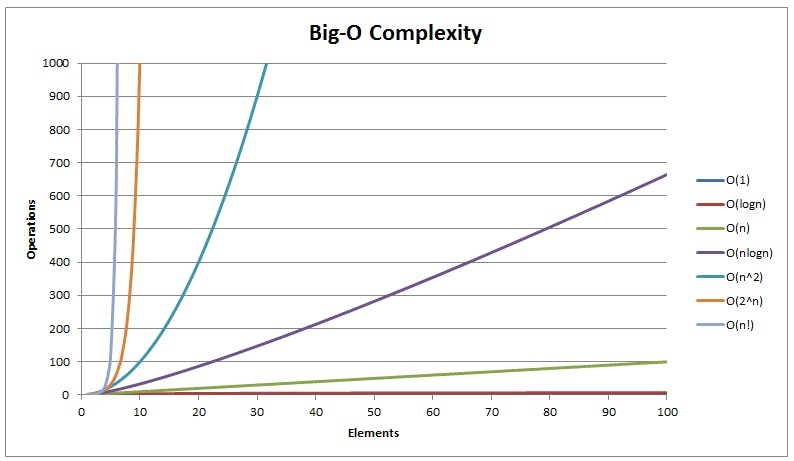
The time complexity of an algorithm is the total amount of time need by an algorithm/code to complete the desired execution. We measure it using Big O notation - Big O notation is a mathematical notation that describes the behavior of a function when the argument tends towards infinity i.e when the input tends to infinity how does our function(code) behaves. It describes the worst-case of an algorithm.
Performance & Optimization
Optimization can be of different types but the 2 most important ones are:
- Optimization for performance
- Optimization for readability and maintainability
For a more beginner level we will only talk about optimization for performance here:
To get started with performance based optimization, the best way is to first start learning any language of your choice thoroughly and how it's libraries work.
Now the question arises - What exactly do you need to learn apart from it's syntax & semantics?
You need to know how things work behind the scenes for example in Java - if suppose we want to add a new element to a list we can either use an array list or a linked list but which one's better?
Let's try to analyze both approaches one by one to see which one works better :
An ArrayList uses an array for storage, and since array is a fixed length data structure, it has to do an operation that copies the array into a new array when you add an element, which means that we need to visit each element of the array atleast one time hence time complexity becomes O(n).
While in a LinkedList, adding an element is no more expensive than finding the last element and assigning a reference and since we already have the reference with us we can just add a new element in constant time i.e O(1).
If you see here we were only able to reach the right conclusion because we knew how array list & linked list works behind the scenes. This is exactly the level you need to reach in order to make a judgement whether or not the approach is good,better or best.

Similarly you need to have a in-depth grasp on other data structures, like HashMaps(Most important) and how Java uses memory and how it control references.
Writing Best code
For a larger picture, the most important part of overall optimized code is to think about both performance and readability/maintainability. If your improvement comes at the cost of a unmaintainable code, it's probably not worth it. On the other hand, if "beautiful" code is not efficient at all, it's not really that beautiful.
My suggestion here would be to get your hands dirty in the languages you are most comfortable with and start doing lot of question on the online sites like hackerank, hackerearth, Leetcode and start understanding the basic data structures.
The reason for this is that these online platforms have a certain limitation on the code you submit, if it takes more than required time it rejects the solution even if it is correct. This way you are bound to optimize the code & eventually if you practice enough, writing optimized code will become your habit.
Moreover if you get stuck somewhere you can go to the discuss panel these websites offer or ask your doubts on stackoverflow/twitter/github discussions. Discussions like these helps a lot.
Over Optimization
Not everytime your optimizations will lead to faster algorithm/code. The reason for this is the big O notation which we discussed earlier.
Calculating complexity using Big O means we are assuming the input parameter is large but this is not always the case.
I have explained this in one of my tweet thread earlier with a simple example. You might want to check that out as well 👇
Other articles that you might like
- GPT-3 - A large open source state-of- the-art language model with more than 175 billion parameters by OpenAI.
- Hyperloglog - An efficient way to find the cardinality of a multiset. It is being used in most of big data systems to compute the count of distinct elements.
- Bloom Filters - An efficient way to find whether an element is present in a set or not
- Merkle Tree - A special data structure with hash pointers.

