What did we discussed in the last article?
In the last article we had a look at basics of GIT. We went through the basic terms associated with git. Also we understood few common commands required to do your first commit. In case you missed out the last article, do give it a read here before proceeding further.
This article will be covering 5 more concepts of git -
1. Branching
Branching is not very tough to comprehend. All the main code of a project is stored in the master branch. Whenever a developer wants to make some changes in the main code base or add a new project module, he/she creates a new branch, make the changes/add new modules to that branch itself, test the code and then merge the branch with master branch.
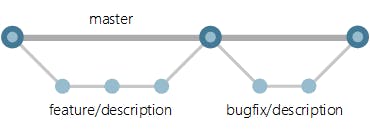
Some branching related git commands-:
git branch
This will lists all local branches in the current repository.
git branch [branch-name]
It will create a new branch with the name you provide.
git checkout [branch-name]
Switches to the specified branch and updates the working directory.
git checkout -b [branch]
It Creates a new branch and switches to it.
git merge [branch]
Combines the specified branch into current branch.
git branch -d [branch-name]
Deletes the specified branch.
2. Go back in time
There are times when you do something terribly wrong & the only way to redo things is to go back in time which seems impossible but with git it's not the case. You can actually go back to the part of the code till which everything was working fine & revert the changes.
As we already know git is used for version control this means you can go to any of your previous versions of your project anytime.
git reflog
By typing this command you will see a list of every thing you've done in git, across all branches! Each one has an index HEAD@{index} find the one before you broke everything and then write.
git reset HEAD@{index}
This command undoes all commits after {index}, preserving changes locally, and change back everything to the specified commit.
3. Pull changes from the origin
We know what push does, pull is simply the opposite of that. In simple language pull is analogous to taking the code from a codebase and merging it to your local codebase.
The command for pulling changes from origin is:
git pull
By default, git uses merge as a pull strategy but there is one more which is rebase, if you want to rebase just write
git pull --rebase origin master
There is only slight difference between merge & rebase, i have explained it in one of my tweet threads -
Basically in this if you have two branches & changes from both these needs to be combined use rebase otherwise both are pretty much the same.
4. Undo that accidental master push
There can be times when you accidentally commit something to master that should have been on a new branch. What to do now?
Just run these 3 commands
git branch [new-branch]
git reset --hard
git checkout [new-branch]
What these 3 commands do is really simple - the first one creates a new branch from the current state of the master branch, the second command resets the branch to the last commit(before you made the blunder 😜) to restore the previous changes, & finally you checkout to the new branch you created.
This way all your changes comes into a new branch without having changed anything from master.
5. Modify origin URL
Sometimes you want to change your origin's url. This happens when the url for your project repo gets changed or modified.
To do this change you need just one command -
git remote set-url origin <new-url>
Conclusion
That concludes the part 2 of this series. I hope you now understand what GIT is and how it can be used. Keep in mind that GIT is a very vast topic and everything can not be put in an article. If you have any doubts or want me to write more about any other topic related to git, we can connect always on Twitter or LinkedIn and I would be happy to answer your queries :)
Other articles that you might like
- Bitcoin Mining - Learn about what exactly bitcoin mining is.
- Improving Time Complexity - Understanding how to improve the time complexity of your code.
- GPT-3 - A large open source state-of- the-art language model with more than 175 billion parameters by OpenAI.

